Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) affects people of all ages, often manifesting in ways that can be mistaken for other conditions or dismissed as personality quirks. Recognizing its signs early can make a significant difference in managing symptoms and improving daily functioning. By understanding the behavioral, physical, and age-specific traits associated with ADHD, individuals can take steps toward seeking appropriate support and treatment. Below, we will explore the key indicators to help identify ADHD.
Common Behavioral Indicators of ADHD

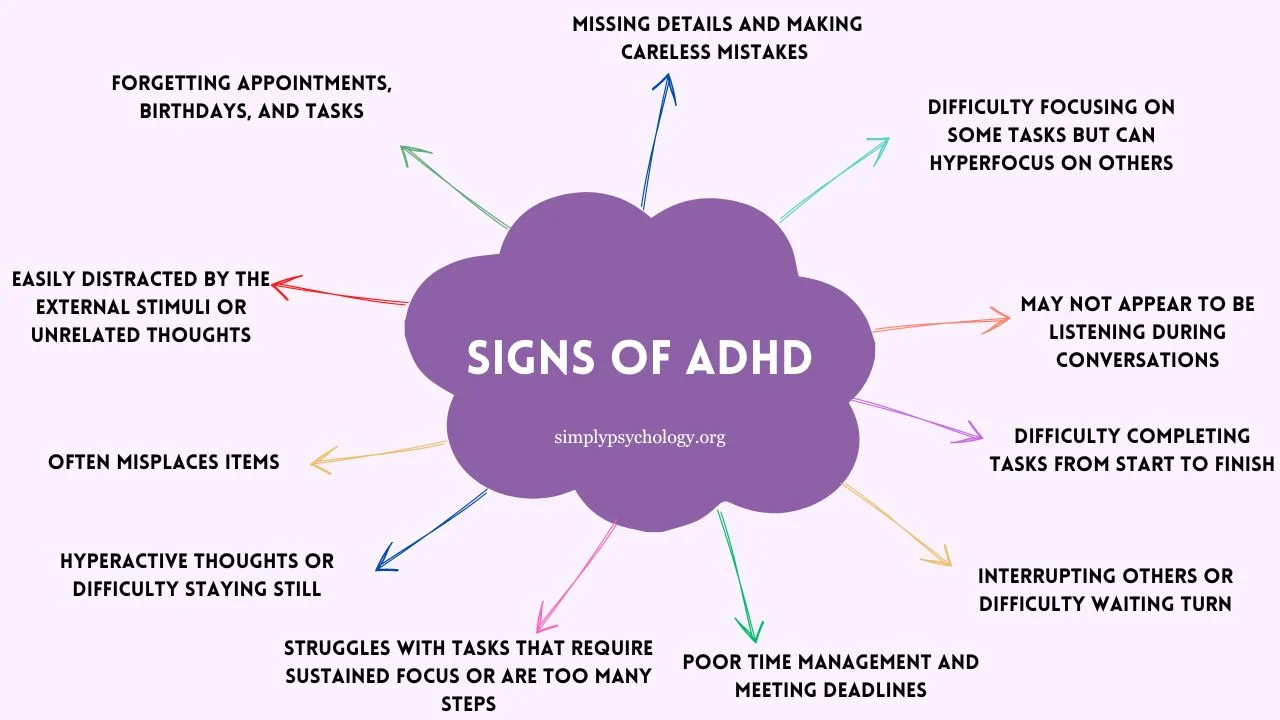
ADHD often presents as a pattern of behaviors that disrupt daily routines, relationships, and work or school performance. One common sign is an inability to focus for extended periods, often called inattentiveness. This may manifest as a tendency to drift off during conversations, lose track of tasks, or struggle with completing detailed assignments. Individuals may find it challenging to follow multi-step instructions, leading to frustration and feelings of inadequacy.
Impulsivity is another hallmark of ADHD and can take many forms. People may interrupt conversations, act without considering consequences, or make rash decisions. This behavior often causes misunderstandings in personal and professional relationships. Impulsivity can also lead to a pattern of starting projects enthusiastically but abandoning them midway due to boredom or distraction.
Hyperactivity is also a key behavioral indicator, though it does not appear in everyone with ADHD. This may involve constant fidgeting, tapping, or the inability to sit still for long periods. In adults, hyperactivity can appear as inner restlessness, where the individual feels like they must always be doing something productive or stimulating. This persistent activity can lead to burnout if left unmanaged.
For those experiencing these behaviors, an ADHD test may be a helpful first step toward understanding your symptoms. These evaluations are designed to identify patterns that suggest ADHD and help rule out other conditions with similar characteristics. Seeking professional guidance is essential for receiving a proper diagnosis and finding effective management strategies.
Physical and Emotional Symptoms to Watch For

Physical restlessness is a common symptom of ADHD, particularly in children. This restlessness can include difficulty remaining seated during meals or in classrooms and a constant need to move or touch objects. In adults, it may manifest as pacing, an inability to relax, or even clumsiness caused by a lack of focus on physical coordination.
Sleep issues are another physical sign that may point to ADHD. People with ADHD often have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to chronic fatigue. This lack of rest exacerbates other symptoms, such as irritability, poor concentration, and decreased productivity. In children, inconsistent sleep patterns can appear as heightened crankiness or mood swings.
Emotionally, individuals with ADHD frequently experience mood instability. Sudden shifts between excitement, frustration, and sadness can occur, often triggered by minor events. This emotional volatility can make it difficult to maintain stable relationships, as others may misinterpret these fluctuations as unpredictability or insensitivity.
Low self-esteem is another emotional symptom tied to ADHD. Because individuals with ADHD often struggle to meet expectations in work, school, or social settings, they may develop feelings of inadequacy or self-doubt. This negative self-perception can be worsened by criticism from others who misunderstand their behavior, creating a cycle of discouragement and withdrawal.
ADHD Traits in Different Age Groups
ADHD traits often appear in children as difficulties with focus and hyperactivity. They may struggle to follow classroom rules, frequently interrupt teachers or classmates, and show excessive energy in challenging group activities. These behaviors are not always recognized as symptoms of ADHD but are crucial to identifying the condition early.
Teenagers with ADHD may experience similar challenges but often face additional obstacles as they deal with increased academic and social pressures. Forgetting assignments, losing personal items, or missing deadlines are common issues. They may also become easily frustrated by tasks requiring sustained mental effort, leading to procrastination or avoidance.
ADHD often manifests differently in adults than in children or teens. While hyperactivity may diminish, inattentiveness and impulsivity often remain prominent. Adults may struggle to stay organized, keep up with responsibilities, or maintain focus during meetings. This can result in difficulty meeting personal and professional goals, leading to frustration and stress.
Seniors with undiagnosed ADHD may notice the effects more acutely as their coping mechanisms weaken with age. Forgetfulness, trouble concentrating, and poor time management can resemble other age-related cognitive changes, making ADHD harder to identify. However, understanding these traits can help older individuals seek appropriate support and improve their quality of life.
Altogether, recognizing the signs of ADHD across behavioral, physical, and age-specific traits is crucial for understanding the condition and seeking proper support. Early identification and intervention can significantly enhance daily functioning and overall quality of life for individuals of all ages.